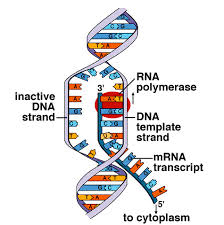
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which the information contained in a section of DNA is replicated in the form of a newly assembled piece of messenger RNA (mRNA). Enzymes facilitating the process include RNA polymerase and transcription factors. In eukaryotic cells the primary transcript is (pre-mRNA). Pre-mRNA must be processed for translation to proceed. Processing includes the addition of a 5' cap and a poly-A tail to the pre-mRNA chain, followed by splicing. Alternative splicing occurs when appropriate, increasing the diversity of the proteins that any single mRNA can produce. The product of the entire transcription process that began with the production of the pre-mRNA chain, is a mature mRNA chain.